- 浏览: 128991 次
- 性别:

- 来自: 广州
-

文章分类
最新评论
-
newhxj:
03-21 10:56:35.850: E/Web Conso ...
Android简易Flash播放器[转] -
roiz:
谢谢 很好正需要这资料
精确监听AbsListView滚动至底部[转]
上一篇简单介绍了SurfaceView的基本使用,这次就介绍SurfaceView与多线程的混搭。SurfaceView与多线程混搭,是为了防止动画闪烁而实现的一种多线程应用。android的多线程用法与JAVA的多线程用法完全一样,本文不做多线程方面的介绍了。直接讲解SurfaceView与多线程的混合使用,即开一条线程专门读取图片,另外一条线程专门绘图。
本文程序运行截图如下,左边是开单个线程读取并绘图,右边是开两个线程,一个专门读取图片,一个专门绘图:
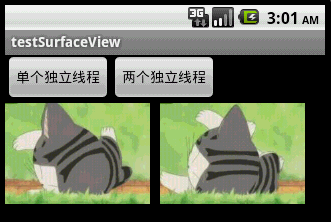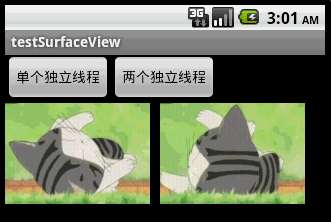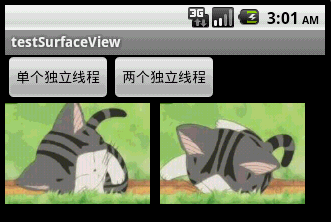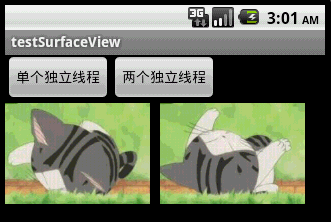
对比一下,右边动画的帧速明显比左边的快,左右两者都没使用Thread.sleep()。为什么要开两个线程一个读一个画,而不去开两个线程像左边那样都“边读边画”呢?因为SurfaceView每次绘图都会锁定Canvas,也就是说同一片区域这次没画完下次就不能画,因此要提高动画播放的效率,就得开一条线程专门画图,开另外一条线程做预处理的工作。
main.xml的源码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:orientation="vertical">
<LinearLayout android:id="@+id/LinearLayout01"
android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content">
<Button android:id="@+id/Button01" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="单个独立线程"></Button>
<Button android:id="@+id/Button02" android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="两个独立线程"></Button>
</LinearLayout>
<SurfaceView android:id="@+id/SurfaceView01"
android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"></SurfaceView>
</LinearLayout>
本文程序的源码:
package com.testSurfaceView;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Bitmap;
import android.graphics.BitmapFactory;
import android.graphics.Canvas;
import android.graphics.Paint;
import android.graphics.Rect;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.SurfaceHolder;
import android.view.SurfaceView;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.Button;
public class testSurfaceView extends Activity {
/** Called when the activity is first created. */
Button btnSingleThread, btnDoubleThread;
SurfaceView sfv;
SurfaceHolder sfh;
ArrayList<Integer> imgList = new ArrayList<Integer>();
int imgWidth, imgHeight;
Bitmap bitmap;//独立线程读取,独立线程绘图
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
btnSingleThread = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.Button01);
btnDoubleThread = (Button) this.findViewById(R.id.Button02);
btnSingleThread.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
btnDoubleThread.setOnClickListener(new ClickEvent());
sfv = (SurfaceView) this.findViewById(R.id.SurfaceView01);
sfh = sfv.getHolder();
sfh.addCallback(new MyCallBack());// 自动运行surfaceCreated以及surfaceChanged
}
class ClickEvent implements View.OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
if (v == btnSingleThread) {
new Load_DrawImage(0, 0).start();//开一条线程读取并绘图
} else if (v == btnDoubleThread) {
new LoadImage().start();//开一条线程读取
new DrawImage(imgWidth + 10, 0).start();//开一条线程绘图
}
}
}
class MyCallBack implements SurfaceHolder.Callback {
@Override
public void surfaceChanged(SurfaceHolder holder, int format, int width,
int height) {
Log.i("Surface:", "Change");
}
@Override
public void surfaceCreated(SurfaceHolder holder) {
Log.i("Surface:", "Create");
// 用反射机制来获取资源中的图片ID和尺寸
Field[] fields = R.drawable.class.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
if (!"icon".equals(field.getName()))// 除了icon之外的图片
{
int index = 0;
try {
index = field.getInt(R.drawable.class);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
// 保存图片ID
imgList.add(index);
}
}
// 取得图像大小
Bitmap bmImg = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),
imgList.get(0));
imgWidth = bmImg.getWidth();
imgHeight = bmImg.getHeight();
}
@Override
public void surfaceDestroyed(SurfaceHolder holder) {
Log.i("Surface:", "Destroy");
}
}
/*
* 读取并显示图片的线程
*/
class Load_DrawImage extends Thread {
int x, y;
int imgIndex = 0;
public Load_DrawImage(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
Canvas c = sfh.lockCanvas(new Rect(this.x, this.y, this.x
+ imgWidth, this.y + imgHeight));
Bitmap bmImg = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),
imgList.get(imgIndex));
c.drawBitmap(bmImg, this.x, this.y, new Paint());
imgIndex++;
if (imgIndex == imgList.size())
imgIndex = 0;
sfh.unlockCanvasAndPost(c);// 更新屏幕显示内容
}
}
};
/*
* 只负责绘图的线程
*/
class DrawImage extends Thread {
int x, y;
public DrawImage(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public void run() {
while (true) {
if (bitmap != null) {//如果图像有效
Canvas c = sfh.lockCanvas(new Rect(this.x, this.y, this.x
+ imgWidth, this.y + imgHeight));
c.drawBitmap(bitmap, this.x, this.y, new Paint());
sfh.unlockCanvasAndPost(c);// 更新屏幕显示内容
}
}
}
};
/*
* 只负责读取图片的线程
*/
class LoadImage extends Thread {
int imgIndex = 0;
public void run() {
while (true) {
bitmap = BitmapFactory.decodeResource(getResources(),
imgList.get(imgIndex));
imgIndex++;
if (imgIndex == imgList.size())//如果到尽头则重新读取
imgIndex = 0;
}
}
};
}
本文来自http://blog.csdn.net/hellogv/article/details/5986835
发表评论
-
android Theme使用总结
2012-12-12 19:22 1424今天对api中style下的theme整个摸了一遍。 ... -
android优化——adapter
2012-12-12 18:56 1469什么是Adapter,可以先看看我的上一篇文章,Andr ... -
listview样式设置——自定义背景、分隔[转]
2012-12-12 14:13 783在Android中,ListView是最常用的一个控件, ... -
draw9patch不失真背景
2012-12-12 00:23 12911.背景自适应且不失真问题的存在 制作自适应背 ... -
android布局之selector(背景选择器)[转]
2012-12-11 23:07 2816关于listview和button都� ... -
android布局之RelativeLayout属性
2012-12-11 23:06 1179android:layout_above � ... -
Android ListView下拉刷新点击加载更多[转]
2012-12-03 09:04 1682这个ListView的下拉刷新算是不错了。网上找了很多个 ... -
BitmapFactory.Options详解[转]
2012-11-21 20:50 3279public Bitmap in ... -
Android简易Flash播放器[转]
2012-01-20 21:16 1871上一节,大体说了下在Android程序中嵌套Flash动 ... -
将flash嵌入你的程序中[转]
2012-01-20 21:12 1135无论如何,我们需要一个android2.2的平板电脑 ... -
Android实现ListView异步加载图片[转]
2011-11-30 11:17 681ListView异步加载图片是非常实用的方法,凡是是要通过网络 ... -
精确监听AbsListView滚动至底部[转]
2011-11-10 09:00 1397用户使用android客户端时,当Lis ... -
可动态布局的Android抽屉之完整篇[转]
2011-11-10 09:00 1070上次介绍了基础篇,讲解了自定义抽屉控件的基 ... -
可动态布局的Android抽屉之基础[转]
2011-11-10 08:59 1565以前曾经介绍过《Android提高第十九篇 ... -
Android提高第二十一篇之MediaPlayer播放网络视频
2011-11-10 08:59 2613上次讲解了MediaPlayer播放网络音 ... -
Android提高第二十篇之MediaPlayer播放网络音频[转]
2011-11-10 08:58 756以前曾经地介绍过MediaPlayer的基本用 ... -
Android提高第十九篇之"多方向"抽屉[转]
2011-11-09 13:35 1173在android上要实现类似Launch的 ... -
Android提高十八篇之自定义Menu(TabMenu)[转]
2011-11-09 13:35 865用过UCWEB-Android版的人都应 ... -
Android提高十七篇之多级树形菜单的实现[转]
2011-11-09 13:35 858在Android里要实现树形菜单,都是用 ... -
Android提高十六篇之使用NDK把彩图转换灰度图[转]
2011-11-09 13:34 1014在Android上使 ...







相关推荐
Android提高第三篇之SurfaceView与多线程的混搭.docx
第3章 用户人机界面 3.1 更改与显示文字标签——TextView标签的使用 3.2 更改手机窗口画面底色——drawable定义颜色常数的方法 3.3 更改TextView文字颜色——引用Drawable颜色常数及背景色 3.4 置换TextView文字——...
第3章 用户人机界面 3.1 更改与显示文字标签——TextView标签的使用 3.2 更改手机窗口画面底色——drawable定义颜色常数的方法 3.3 更改TextView文字颜色——引用Drawable颜色常数及背景色 3.4 置换TextView文字——...
第3章 用户人机界面 3.1 更改与显示文字标签——TextView标签的使用 3.2 更改手机窗口画面底色——drawable定义颜色常数的方法 3.3 更改TextView文字颜色——引用Drawable颜色常数及背景色 3.4 置换TextView文字——...
第3章 用户人机界面 3.1 更改与显示文字标签——TextView标签的使用 3.2 更改手机窗口画面底色——drawable定义颜色常数的方法 3.3 更改TextView文字颜色——引用Drawable颜色常数及背景色 3.4 置换TextView文字——...
第3章 用户人机界面 3.1 更改与显示文字标签——TextView标签的使用 3.2 更改手机窗口画面底色——drawable定义颜色常数的方法 3.3 更改TextView文字颜色——引用Drawable颜色常数及背景色 3.4 置换TextView文字...
第3章 用户人机界面 3.1 更改与显示文字标签——TextView标签的使用 3.2 更改手机窗口画面底色——drawable定义颜色常数的方法 3.3 更改TextView文字颜色——引用Drawable颜色常数及背景色 3.4 置换TextView文字——...
第3章 用户人机界面 3.1 更改与显示文字标签——TextView标签的使用 3.2 更改手机窗口画面底色——drawable定义颜色常数的方法 3.3 更改TextView文字颜色——引用Drawable颜色常数及背景色 3.4 置换TextView文字——...
) 2.3 Android应用程序架构——从此开始 2.4 可视化的界面开发工具 2.5 部署应用程序到Android手机 第3章 用户人机界面 3.1 更改与显示文字标签——TextView标签的使用 3.2 更改手机窗口画面底色——drawable定义...
第3章 用户人机界面 3.1 更改与显示文字标签——TextView标签的使用 3.2 更改手机窗口画面底色——drawable定义颜色常数的方法 3.3 更改TextView文字颜色——引用Drawable颜色常数及背景色 3.4 置换TextView文字——...
第3章 用户人机界面 3.1 更改与显示文字标签——TextView标签的使用 3.2 更改手机窗口画面底色——drawable定义颜色常数的方法 3.3 更改TextView文字颜色——引用Drawable颜色常数及背景色 3.4 置换TextView文字——...